
If Abs(Range(“DSRA_Copy_Sum”).Cells(1, 1)-Range(“DSRA_Copy_Paste”).Cells(1, 1)) <= 1 Then Exit For Selection.PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues, Operation:=xlNone,SkipBlanks _:=False, Transpose:=False
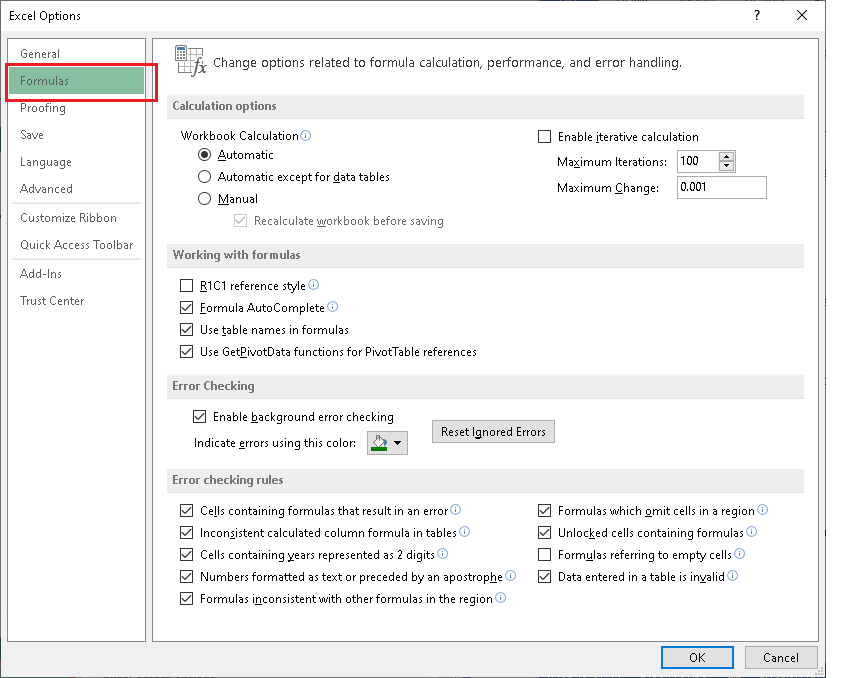
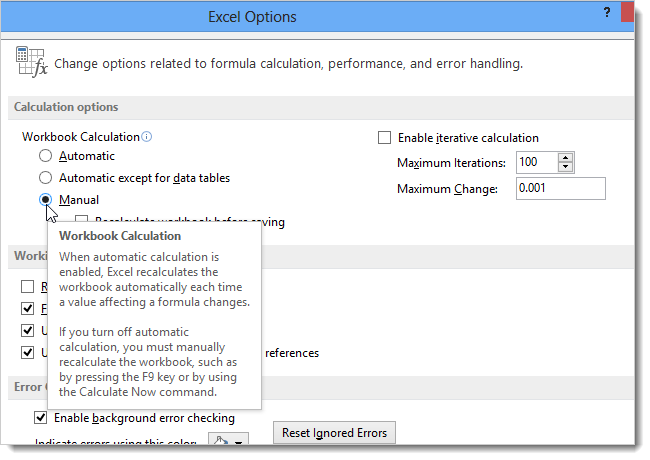
The DSRA is sized as equal to the next 6 month’s debt service, which is in turn a function of the total debt amount, which is a function of, inter alia, the size of the DSRA… The DSRA is funded by a draw down at Commercial Operation Date (COD).The following example shows how you can use the GemBox.Spreadsheet calculation engine to calculate Excel cell formula values in C# and VB.NET.Circular references arise naturally in project models.Įxamples of typical circular references include: ExcelFile.Calculate - Calculates all the cells in an Excel file.Īfter calculating the formulas, you can access the evaluated value using the ExcelCell.Value property.ExcelWorksheet.Calculate - Calculates all of the cells in a single worksheet.ExcelCell.Calculate - Calculates a single cell formula and its references, if any.To calculate the results of the formulas, you need to call one of the following Calculate methods: You can recalculate the formulas that are read from the Excel file and the ones you add at runtime using the ExcelCell.Formula property. The calculation engine also supports iterative calculations, named range references, external references, array formulas, and more. About ~200 of the most used Excel formulas are currently supported but note that we are continuously adding more based on user feedback. For a complete list visit the Supported formulas section.

GemBox.Spreadsheet supports a large set of Excel formula functions, including Mathematical, Statistical, Logical, Lookup, Financial and more.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
